What Increases The Price Sensitivity Of A Bond To Changes In Interest Rates
What is Interest Rate Sensitivity?
Involvement rate sensitivity is the analysis of fixed income security price fluctuations to changes in the market involvement rate. The higher the security's interest charge per unit sensitivity, the greater the price fluctuations.

Summary
- Interest rate sensitivity is the analysis of fixed income security price fluctuations to changes in the market interest rate.
- It is an of import consideration when selling and ownership fixed income on the secondary market.
- Interest rate sensitivity is affected by factors such as the asset's maturity length and coupon rate.
Understanding Interest Rate Sensitivity
Fixed income is i of the major asset classes available to investors. Investors profit from fixed income through the interest (coupon) rate and price appreciation. Fixed income coupon payments are fixed over the life of the security, while toll fluctuations are a direct effect of market place interest charge per unit changes.
Stock-still income securities are created and initially sold on the master market. Next, investors can choose to hold the fixed income security until maturity or resell it on the secondary market. Fixed income cost is negatively correlated with the market involvement rate – this is known as interest rate risk.
At issuance, coupon bonds are sold at par value based on the prevailing marketplace involvement rate. Once the bond is issued, the coupon payments are fixed over the life of the loan, but the market interest rate fluctuates continuously.
When the marketplace interest rate increases, the outstanding stock-still-income security prices depreciate because newly issued fixed-income securities will pay higher coupon payments. Vice versa, if the market interest charge per unit decreases, the outstanding fixed income prices capeesh considering its coupon payments are college than newly issued fixed income securities.
Therefore, understanding involvement rate sensitivity becomes an important consideration in selecting stock-still-income securities. Certain characteristics affect a security's interest rate sensitivity, such as:
ane. Maturity Length
The longer the maturity is, the college the security's interest rate sensitivity. This is considering longer-term securities have college exposure to interest rate gamble .
ii. Coupon Rate
The lower the coupon rate, the higher the security's interest rate sensitivity considering information technology will have higher involvement rate take chances.
How to Measure Interest Rate Sensitivity
To measure involvement rate sensitivity, duration is a keen metric considering it takes such characteristics into consideration. The general dominion of thumb is the higher the duration, the higher the interest rate sensitivity. The 3 almost common types of elapsing are:
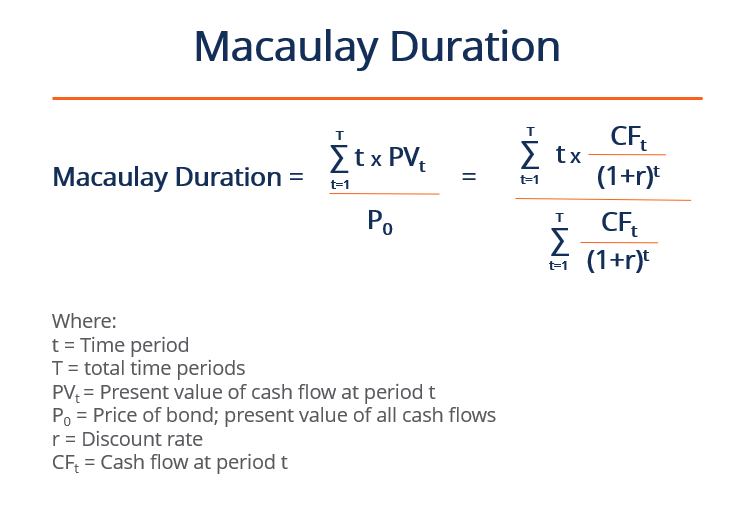
1. Macaulay Duration
The Macaulay duration represents the length of time the investor must hold the security until its total greenbacks flows can repay the bond'south price. For coupon-paying bonds, the Macaulay duration is always shorter than its fourth dimension to maturity. With nil-coupon bonds (bonds without coupon payments that are sold at a discount), the Macaulay duration is equal to its fourth dimension to maturity.
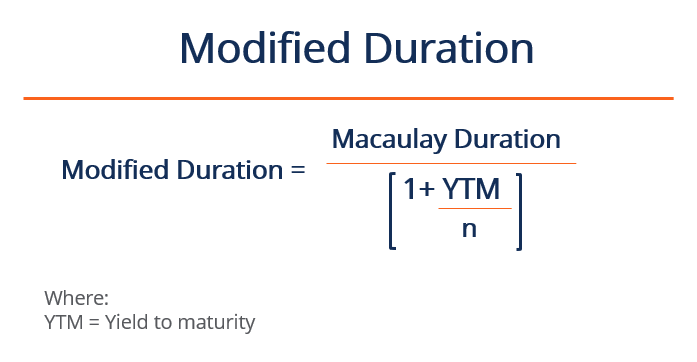
2. Modified Duration
The Modified duration builds on the Macaulay duration by integrating the yield to maturity. Information technology represents the percentage change in bail price in relation to the pct change in the interest charge per unit.
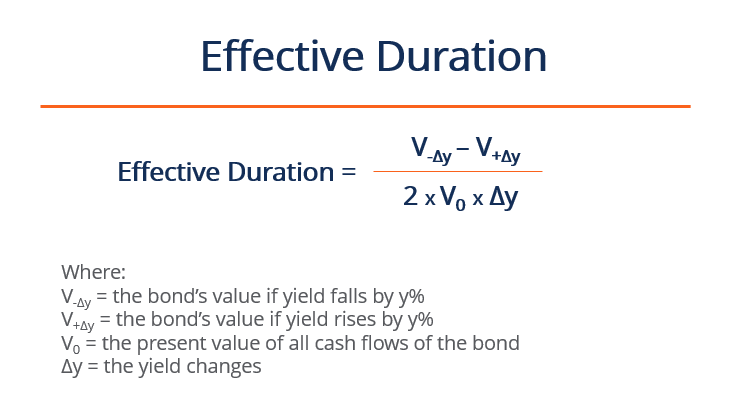
iii. Effective Duration
The constructive duration is practical specifically to bonds with embedded options to account for its uncertainty of future cash flows. The effective duration serves as the percentage change in price relative to the percentage change in yield to maturity.
Applied Example
Suppose an investor purchases a $two,000 par value bond with a 2.5% coupon rate compounded annually. The maturity appointment is iv years from today, on which the principal $2,000 will be returned. What is the Macaulay elapsing of the bond?
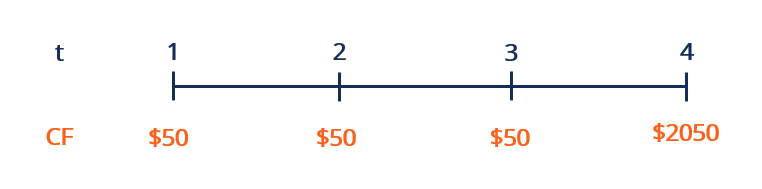
While the formula may look intimidating, the numerator and the denominator are almost identical, except each cash flow in the numerator is multiplied by its respective time flow t. For the discount rate r, we are using the coupon rate of the bond.
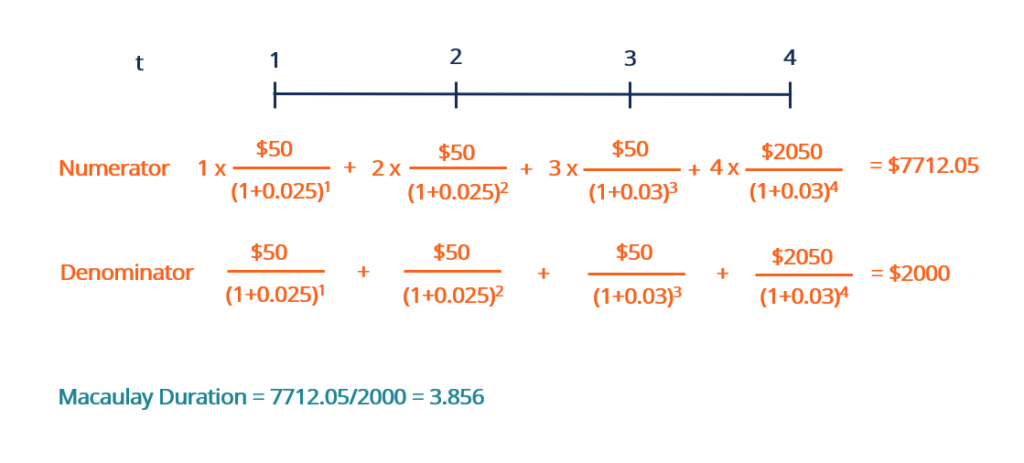
With the numerator and denominator solved, nosotros put those together to get a Macaulay duration of three.856. It means that it will have approximately 3.856 years of holding the bail for its greenbacks flows to cover its price. Considering the bond pays coupon payments, the Macaulay duration is shorter than its time to maturity of four years.
Learn More
CFI offers the Uppercase Markets & Securities Analyst (CMSA)® certification programme for those looking to take their careers to the next level. To go along learning and accelerate your career, the following resource volition exist helpful:
- Bond Pricing
- Secondary Market
- Sensitivity Assay
- Yield to Maturity (YTM)
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/trading-investing/interest-rate-sensitivity/
Posted by: alvarezbardid.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Increases The Price Sensitivity Of A Bond To Changes In Interest Rates"
Post a Comment